MTA-STS and DANE
Carsten Strotmann - Patrick Koetter, sys4 AG
Created: 2023-10-20 Fri 07:05
MTA-STS
What is MTA-STS
- Mail-Transfer-Agent Strict-Transport-Security (MTA-STS, RFC 8461 Standards Track) is an alternative approach to secure TLS connections for SMTP communication
MTA-STS idea
- A special DNS TXT record signals the existence of an TLS policy for
one or more mail server for a given mail domain
- The TLS policy is stored on an TLS secured web-server (HTTPS 1.2 or higher required)
The MTA-STS DNS TXT record
- The MTA-STS TXT record is stored with the label
_mta-stsat the mail-domain for which a policy should be defined - For the domain
example.orgthat would be a TXT record at the domain name_mta-sts.example.org
Example of an MTA-STS record
; <<>> DiG 9.16.44-Debian <<>> _mta-sts.microsoft.com txt [...] ;; ANSWER SECTION: _mta-sts.microsoft.com. 3564 IN TXT "v=STSv1; id=20210331000000Z;"
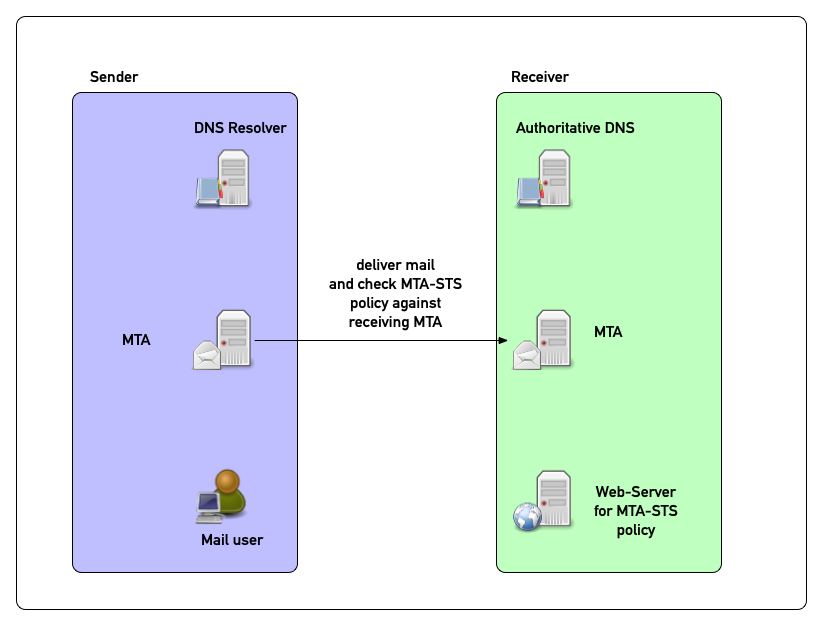
MTA-STS in pictures
MTA-STS in pictures (1)
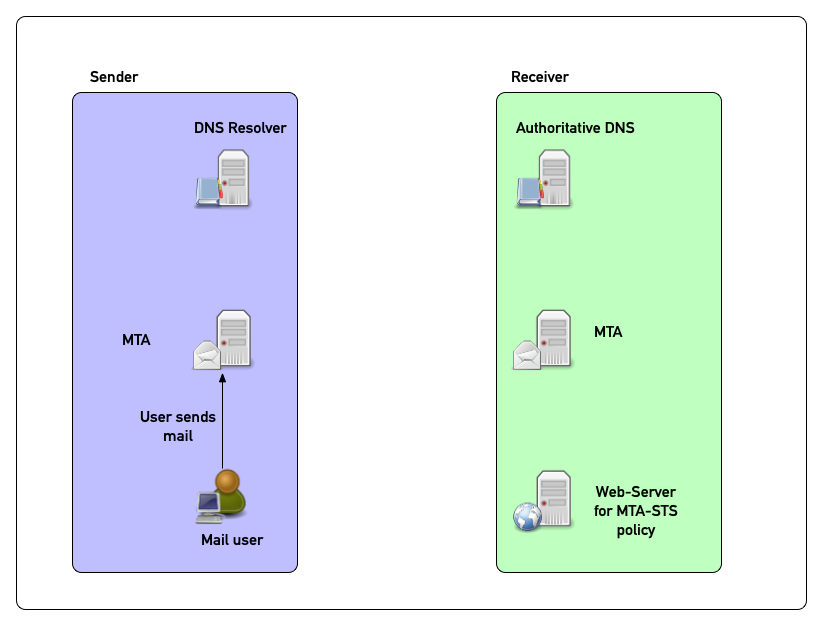
MTA-STS in pictures (2)
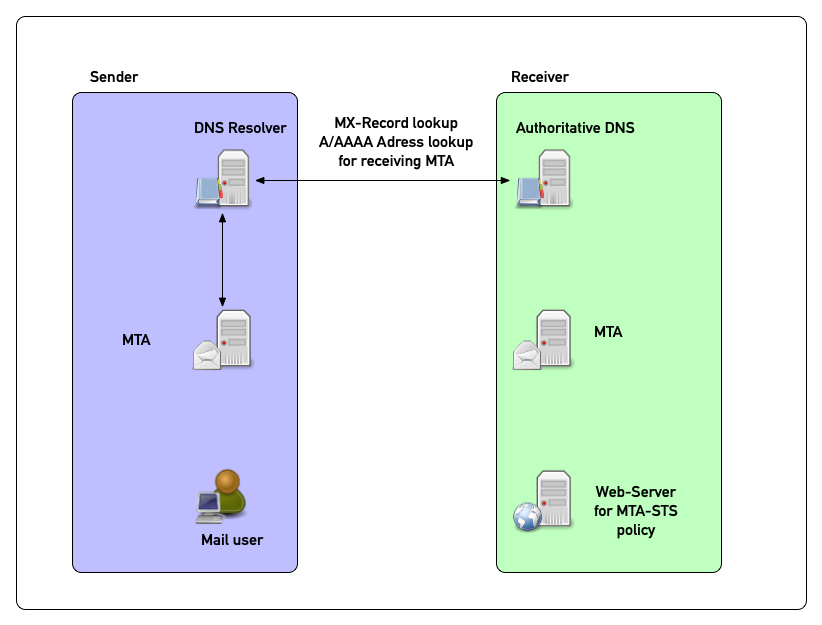
MTA-STS in pictures (3)
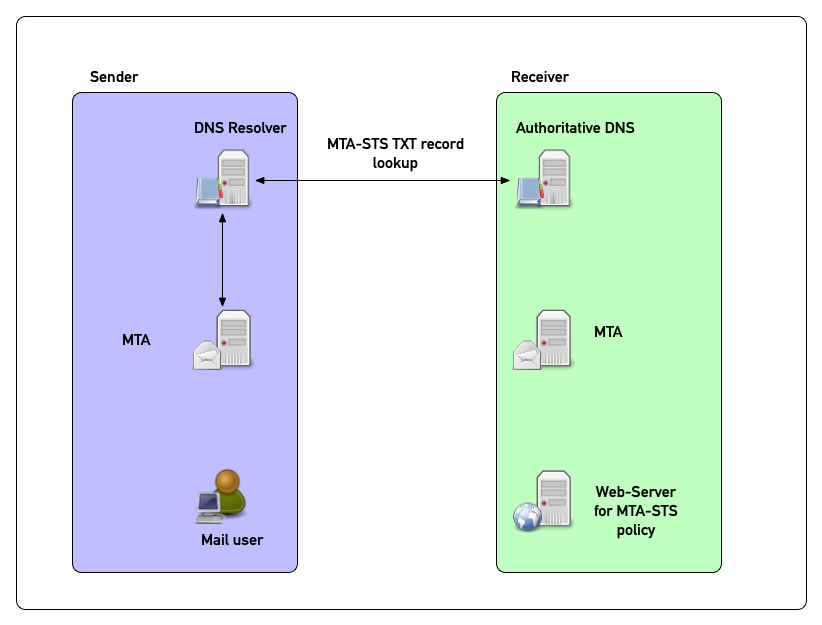
MTA-STS in pictures (4)
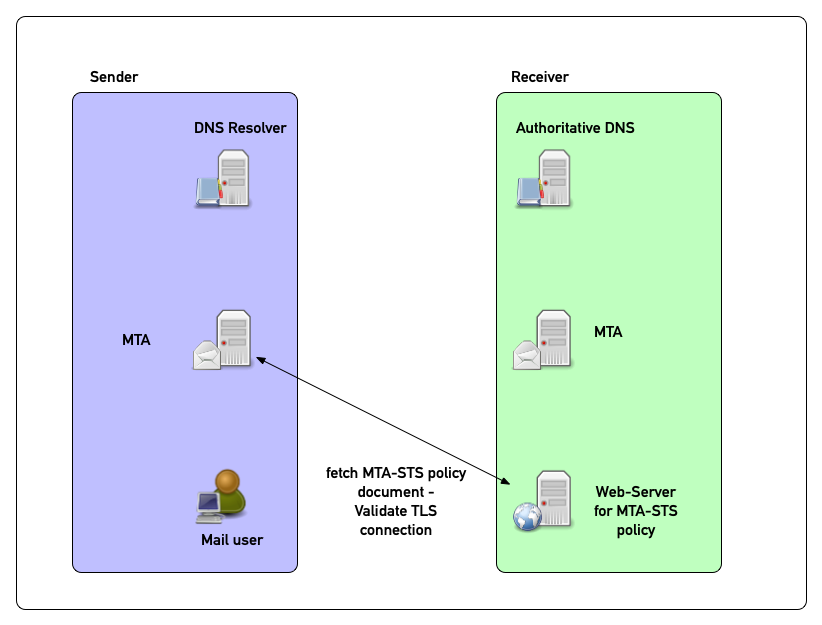
MTA-STS in pictures (5)
MTA-STS TXT record
Anatomy of the MTA-STS TXT record
- The MTA-STS TXT record contains two fields, separated and
terminated by semicolon
;- A Version number of the MTA-STS protocol, currently only the
value
STSv1is defined - An ID of the current policy. This ID is being used to check for changes of the policy document on the web-server. The ID value is an opaque value, its contents has no meaning to the MTA-STS protocol. A change of the ID value will trigger a reload of the MTA-STS policy from the server
- The existence of a TXT record on the domain name
_mta-stssignals a MTA-STS policy on the webserver with the namemta-sts(no underscore in the name of the web-server!)
- A Version number of the MTA-STS protocol, currently only the
value
MTA-STS policy document
MTA-STS policy document location
- The MTA-STS policy document is served by a web-server with TLS 1.2
(or better) transport security under the
name
mta-stsinside the mail domain- For the mail-domain
example.org, the web-server would be namedmta-sts.example.org. - The document is named
mta-sts.txtand is located under the.well-knownpath - The document must be served as mime-type
text/plain - The full URL for
expample.orgwould behttps://mta-sts.example.org/.well-known/mta-sts.txt
- For the mail-domain
MTA-STS policy document content
- The policy document contains key/value pairs (each one line)
Example of a real world MTA-STS policy file
% curl https://mta-sts.microsoft.com/.well-known/mta-sts.txt version: STSv1 mode: enforce mx: *.mail.protection.outlook.com max_age: 604800
MTA-STS policy fields (1/2)
- Version: value
STSv1 - Mode:
none: no policy should be enforced. This value can be used to migrate away from an active MTA-STS policytesting: the policy is not enforced, but violations against the policy should be reported via TLS-Reporting (TLS-RPT, RFC 8460)enforce: The MTA-STS policy must be enforced by sending MTAs, mail can only be delivered with transport security enabled and verified
MTA-STS policy fields (2/2)
- MX: incoming mail server domain name values for pattern matching - either full qualified domain
names of receiving mail servers or wildcard domain names with
*as the leftmost label- this value defines the names of incoming mail server for this mail domain
- multiple
mxlines can exist
- MAX-AGE: maximum lifetime of this policy in seconds (max value 31.557.600 seconds = 1 year). This value is being used by sending MTAs to control the caching of the policy
MTA-STS security
- MTA-STS does not mandate DNSSEC security for the lookup of the
MTA-STS TXT record
- Attacker can disable MTA-STS by blocking/removing DNS lookups
- The use of HTTPS as a policy channel enables new types of denial-of-service attacks against the mail infrastructure
MTA-STS and DANE
- Security: DANE does not allow downgrade-attacks (because it mandates DNSSEC), MTA-STS can be disabled by DNS attacks when not DNSSEC secured
- Caching: DANE uses DNS as its caching layer, MTA-STS requires an extra caching infrastructure in each MTA
- Complexity: The additional HTTPS/Web component increases the complexity of the MTA software and enables new attack vectors against mail server software
MTA-STS and DANE
- MTA-STS and DANE can both be deployed for a mail domain
- When there are conflicting information from DANE and MTA-STS, the DANE information has priority (more secure) and MTA-STS cannot be used to override DANE
- Whenever possible, DANE should be preferred over MTA-STS
End
Questions? / Answers!